What is image SEO?
Image SEO refers to the practice of optimizing your images for search engines through thoughtful alt text, appropriate captions, good file dimensions, and more. Image SEO can make your content easier to interpret by search engine crawlers, which can give it an SEO boost on both search results pages and image results pages and make your site more discoverable.
Visual SEO refers to the optimization of visual content, such as images and videos, for search engines to improve their visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs). While traditional SEO focuses primarily on text-based content, visual SEO aims to optimize images and other visual elements to attract organic traffic from search engines. Optimizing images for Google visibility involves several strategies, including:
- File Name Optimization: Use descriptive file names that include relevant keywords. For example, instead of “DSC12345.jpg,” use “red-running-shoes.jpg” if the image depicts red running shoes.
- Alt Text: Write descriptive alt text that accurately describes the content of the image and includes relevant keywords. Alt text helps search engines understand the context of the image and improves accessibility for users.
- Image Size and Format: Compress images to reduce file size without sacrificing quality. Choose the appropriate image format (JPEG, PNG, GIF) based on the type of image and its intended use on the website.
- Image Dimensions: Resize images to fit the dimensions of your website and optimize loading times. Avoid using oversized images that may slow down page loading speed.
- Contextual Relevance: Surround images with relevant text to provide context to search engines. Use keywords in the surrounding text to reinforce the relevance of the image to the overall content of the page.
- Image Sitemaps: Create an image sitemap and submit it to Google Search Console to help search engines discover and index your images more effectively.
- Responsive Design: Ensure that images are optimized for mobile devices and responsive to different screen sizes. Google prioritizes mobile-friendly websites in its search results.
- Metadata Optimization: Fill in metadata fields such as title, caption, and description with relevant keywords to provide additional context to search engines.
- Original Content: Use original images whenever possible, as opposed to stock photos or images that are widely used across the web. Original content is more likely to stand out in search results.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor the performance of your images in Google Search Console and other analytics tools. Pay attention to metrics such as impressions, clicks, and click-through rates to identify areas for improvement.
As for programs that can be used to compress images, there are several options available, including:
- Adobe Photoshop: Offers various compression options and settings to reduce image file size while maintaining quality.
- GIMP (GNU Image Manipulation Program): A free and open-source alternative to Photoshop that also provides image compression features.
- Online Tools: Websites like TinyPNG, JPEG Optimizer, and Compressor.io allow you to upload and compress images directly in your web browser.
- Image Editing Software: Many image editing software programs, such as Affinity Photo and Corel PaintShop Pro, include built-in image compression features.
By implementing these strategies and using appropriate tools, you can optimize your images for Google visibility and improve your website’s search engine rankings.
Backlinking opportunities of Images
Creating high-quality, unique, original images isn’t just great for your own website — it’s also a fantastic opportunity to earn backlinks when other websites use your image for their own pages.
For instance, consider the following graph created by Broadband Search:
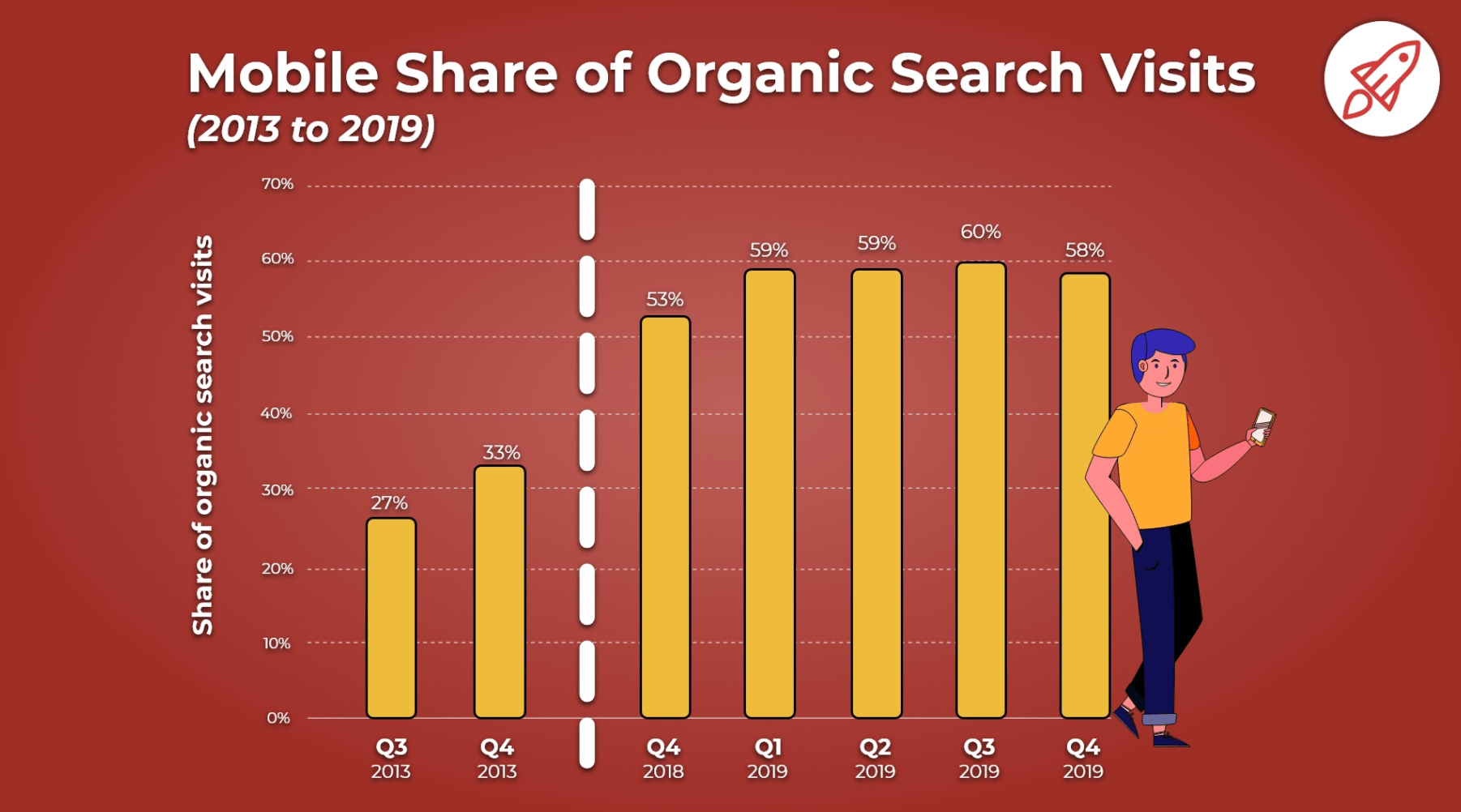
The image currently ranks in the first spot on the image search results page for the keywords, “how many people use mobile to search”.
Additionally, according to Ahrefs, this blog post has over 3,000 backlinks. I’m willing to bet that those backlinks are, in part, due to other companies wanting to use Broadband Search’s unique graphs for their own content.
If you create high-quality images, other companies may want to showcase those images on their own sites — with links back to your business. This means, ultimately, images can have a direct impact on the amount of traffic, leads, and customers you get for your business through your marketing efforts.
Adding images to an existing sitemap.
Google suggests adding images to an existing sitemap — or creating a separate sitemap just for images — to help search engines discover your images. In particular, this is helpful for images Google can’t find through crawling, such as those accessed via JavaScript forms.
Here’s a sample sitemap, with two images included:

Fortunately, if you don’t want to add images to a sitemap manually, you’re in luck — there are tools, such as Angeldigital.Marketing (one of the only free ones available!), that will automatically generate an image sitemap once you input a URL.
Hopefully, you can use these best practices to level up and earn new traffic through search image results pages. Remember, a picture is worth a thousand words … so just imagine the value of an SEO-optimized picture.



